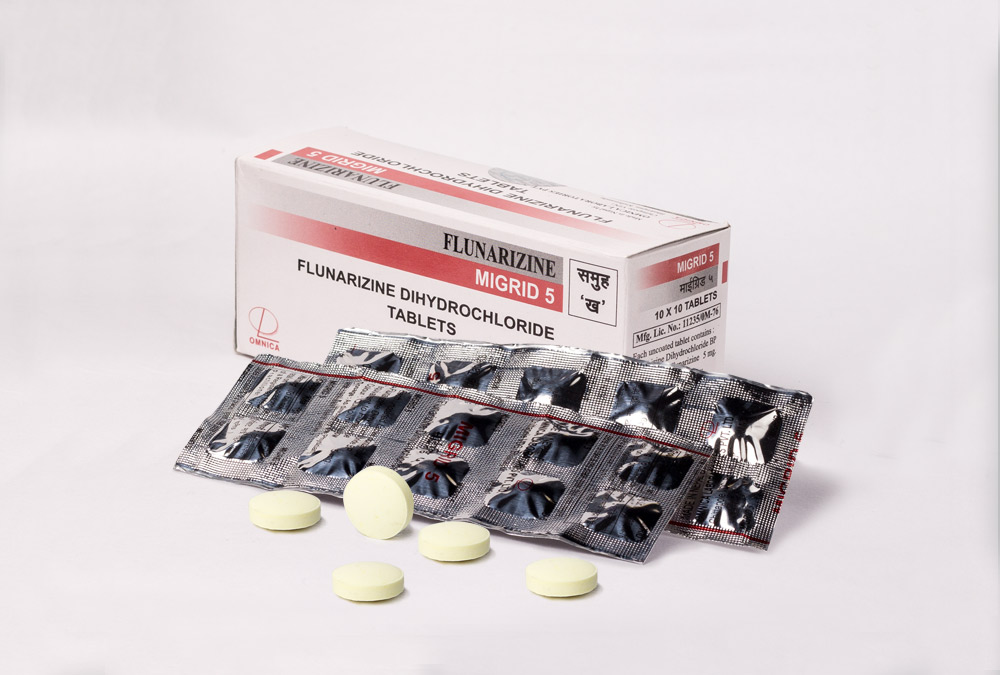
Brand Name : MIGRID
Generic Name : Flunarizine
Preparations : 5 mg / 10 mg Tablets
Pharmacological Categories : Histamine H1 Antagonist, Calcium Channel Blocker, Vasodilator, Anticonvulsant
Mechanism of Action (MOA)
MIGRID (Flunarizine) has antihistamine, sedative and calcium channel blocking activity.
The possible mechanisms of MIGRID are inhibition of vasospasm induced by mediators such as serotonin and prostaglandins, inhibition of cellular hypoxia and improved blood viscosity and erythrocyte deformability.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption : Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract
- Peak Plasma Concentrations : 2 to 4 hours
- Protein Binding : More than 90%.
- Metabolism : Liver
- Excretion : Metabolites are excreted principally in the bile
- Elimination Half-life : About 18 days
Indications and Dosage
Migraine Prophylaxis, Vertigo and Vestibular Disorders, Peripheral and Cerebral Vascular Disorders : One tablet of MIGRID 5 or 10 mg daily given at night to minimize the effects of drowsiness
Side Effects
COMMON : Drowsiness, lassitude, dizziness, incoordination, headache, psychomotor impairment, dry mouth, thickened respiratory tract secretions, blurred vision, urinary difficulty or retention, constipation, increased gastric reflux
OCCASSIONAL : Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, epigastric pain, palpitation, arrhythmia
SEEN : Weight gain, extrapyramidal symptoms (sometime associated with depression)
RARE : Galactorrhoea
Contraindications
Depressive illness, history of recurrent depression, pre-existing symptoms of Parkinson’s disease or other extrapyramidal disorders
Warnings / Precautions
- Drowsiness is a major problem and those affected should not drive or operate machinery.
- Alcohol should be avoided.
- Flunarizine should be used with care in conditions such as angle-closure glaucoma, urinary retention, prostatic hyperplasia, pyloroduodenal obstruction.
- Caution in patient with epilepsy, hepatic impairment.
Drug Interactions
- Hepatic enzyme inducers such as carbamazepine, phenytoin and valproate may increase metabolism of flunarizine.
- Flunarizine may enhance the sedative effects of CNS depressants including alcohol, barbiturates, hypnotics, opioid analgesics, anxiolytic sedatives and antipsychotics.
- Additive antimuscarinic action with other antimuscarinic drugs such as atropine and some antidepressants (both tricyclics and MAOIs)
Pregnancy Category : C
Presentations
MIGRID 5 mg : A box of 10 strips, each strip of 10 tablets
MIGRID 10 mg : A box of 10 strips, each strip of 10 tablets